Left Posterior Fascicular Block Treatment
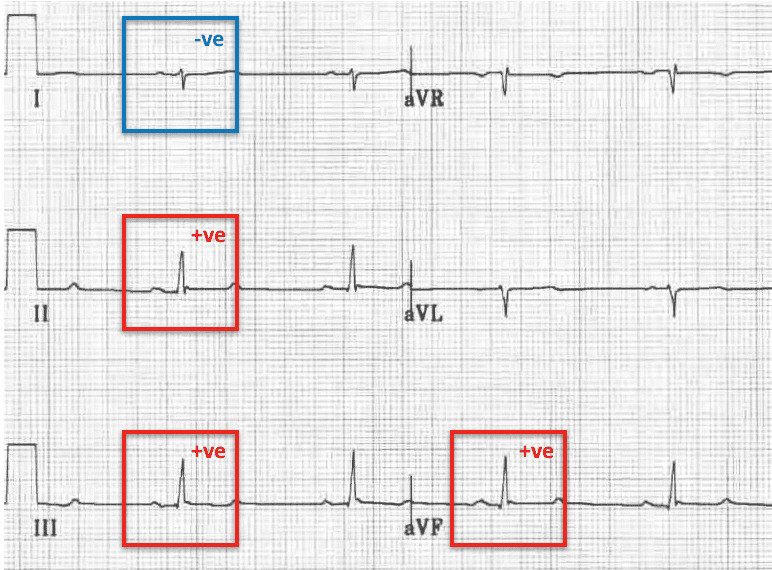
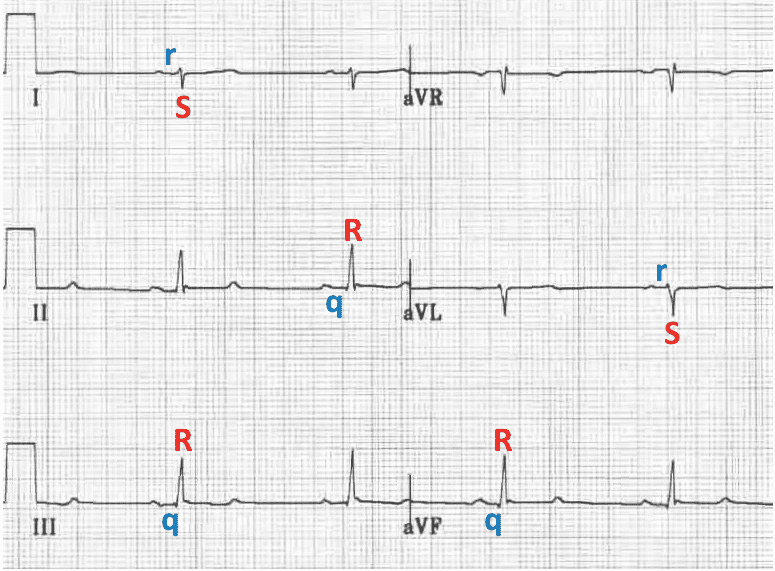
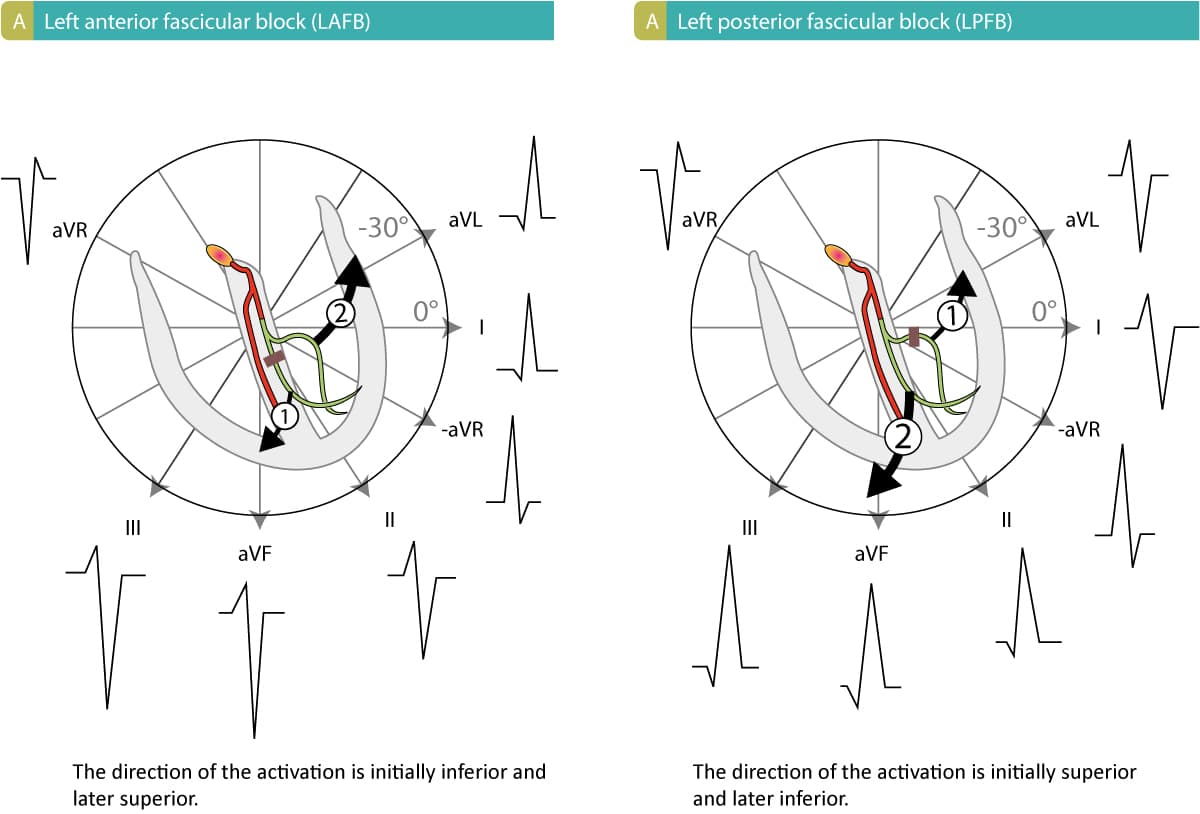
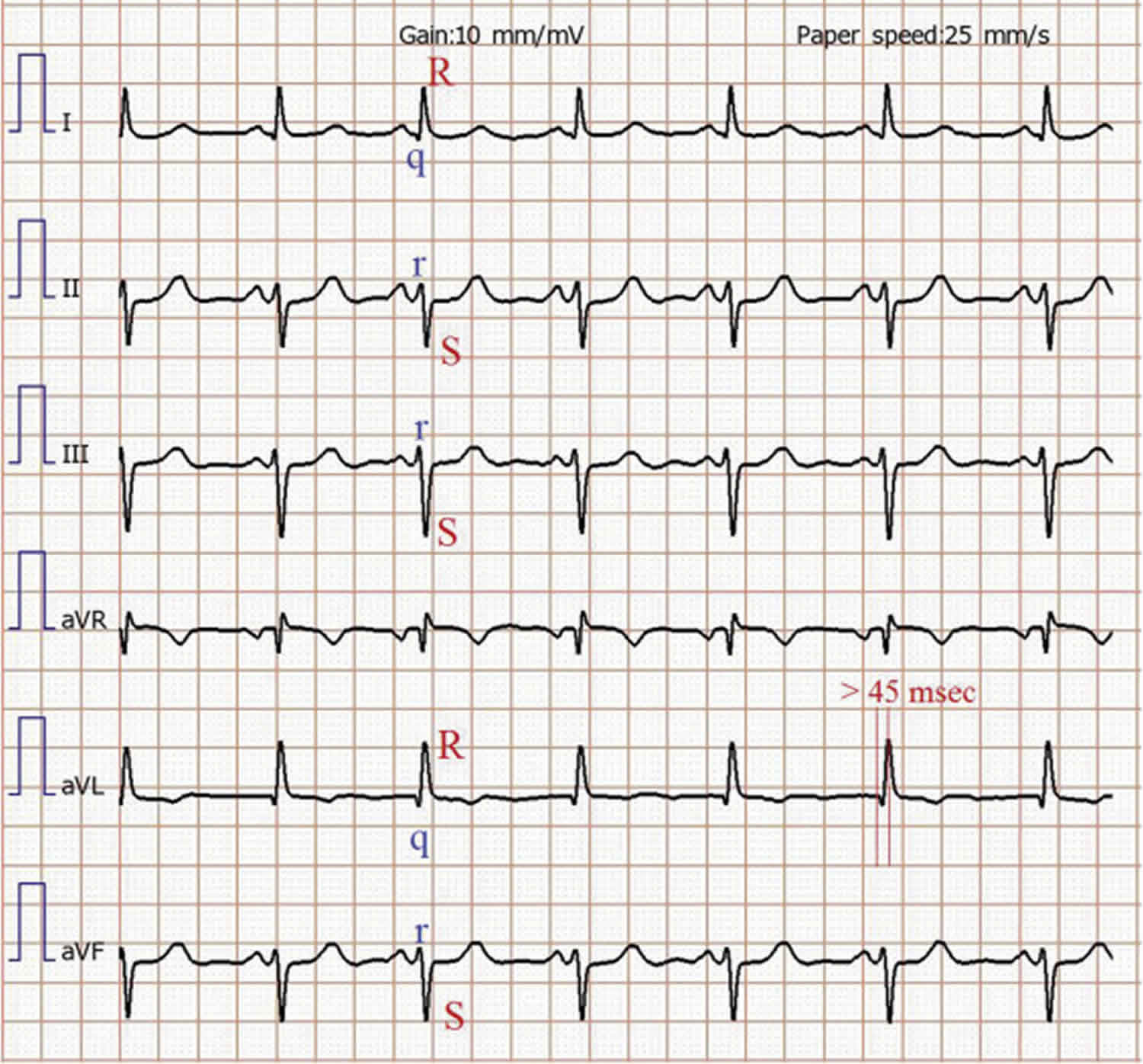
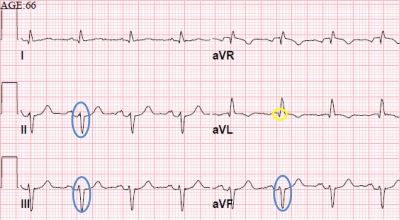
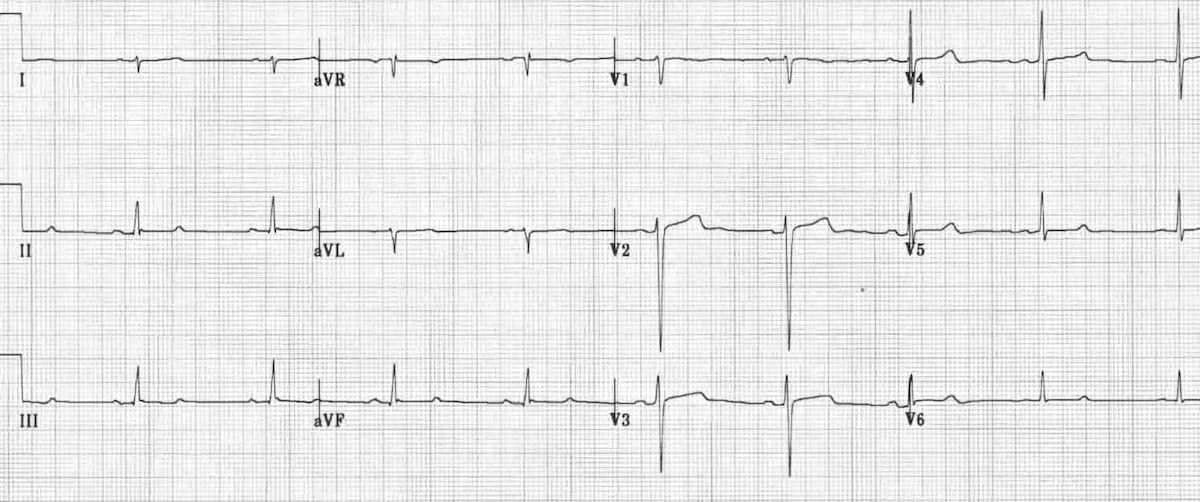
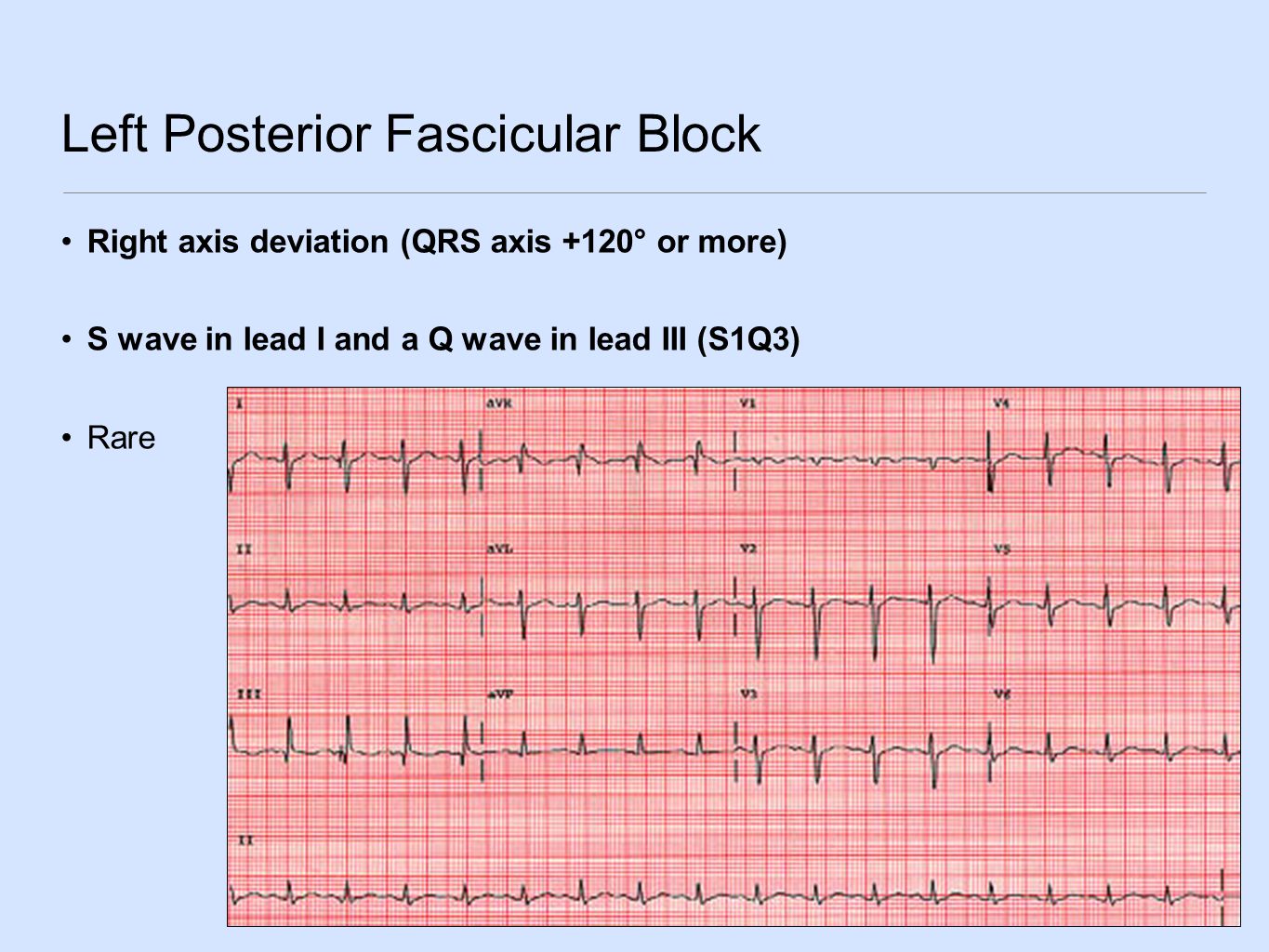
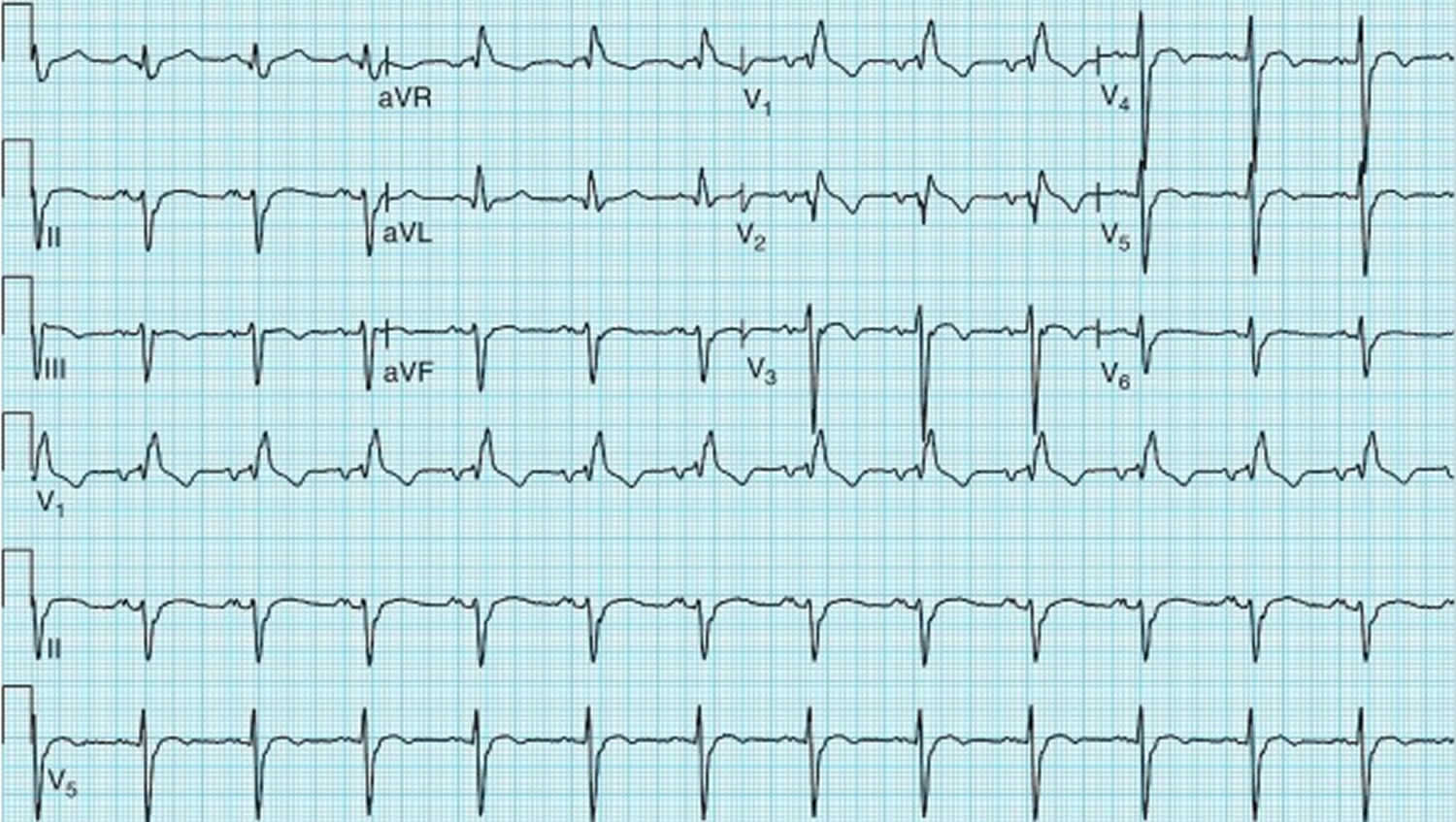
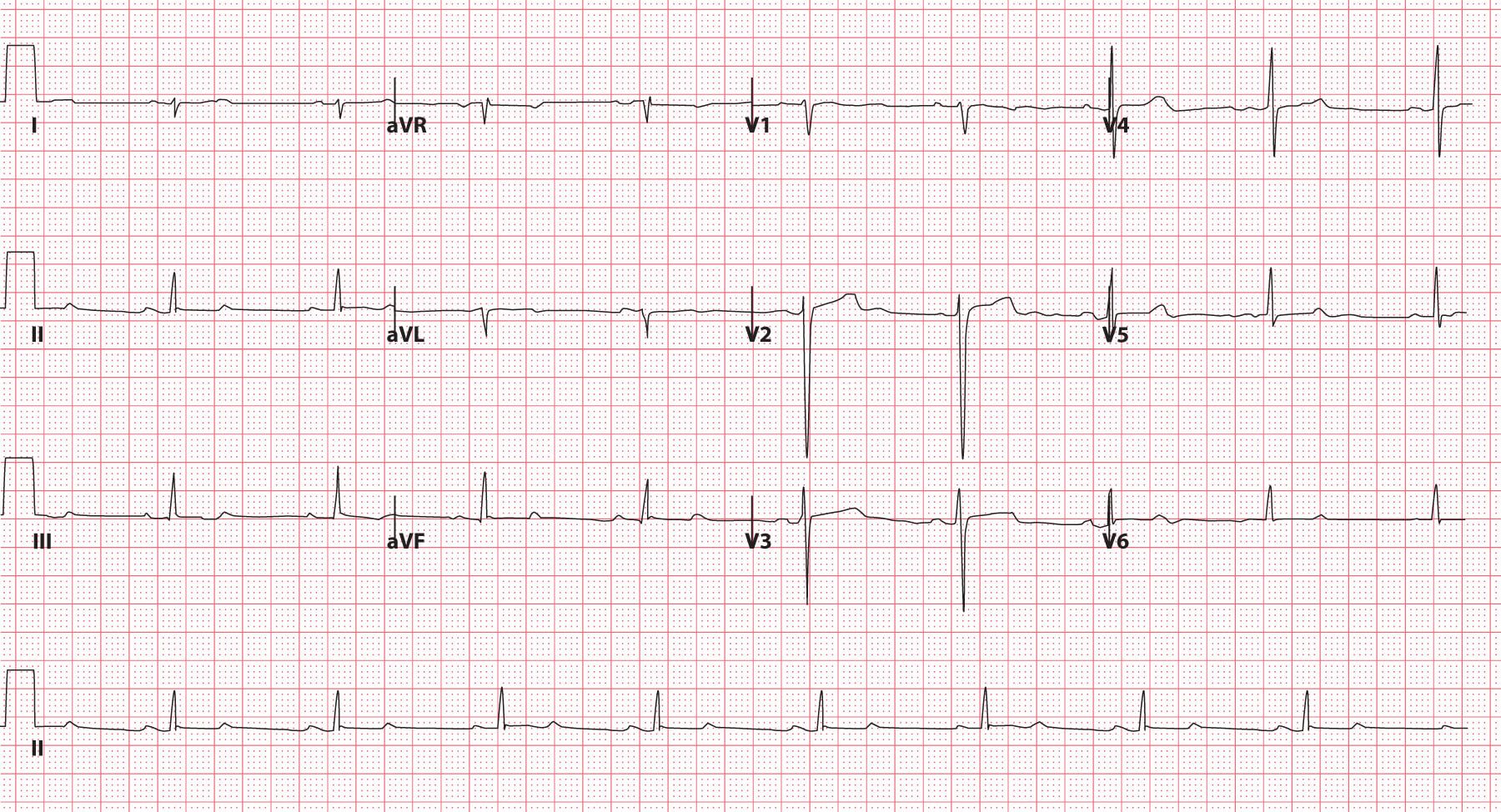
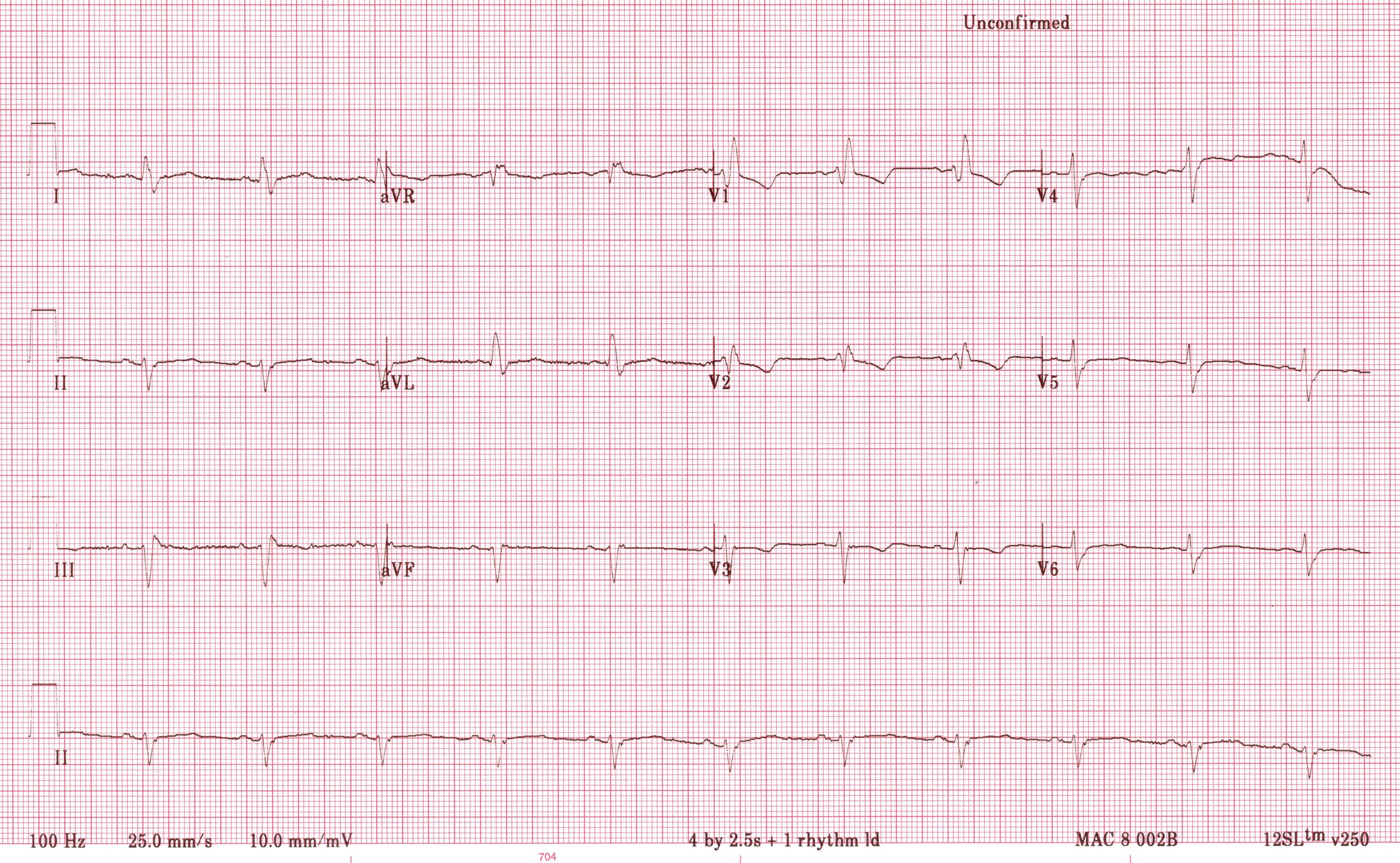
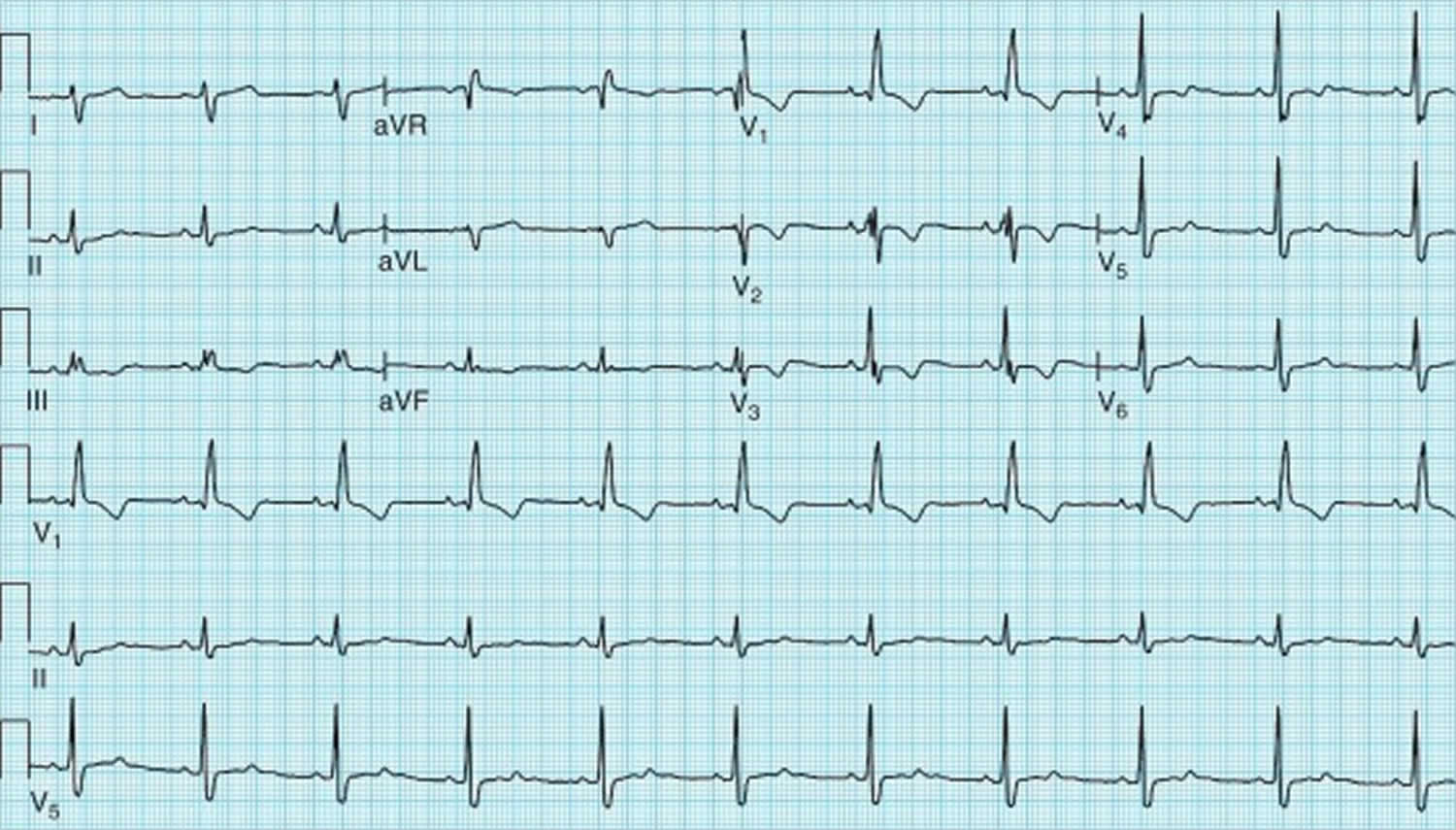
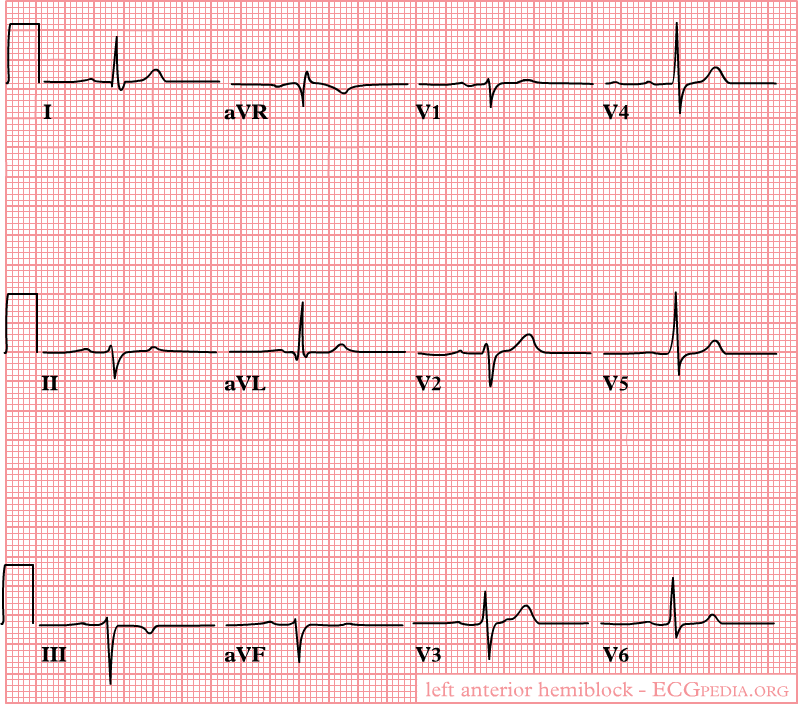
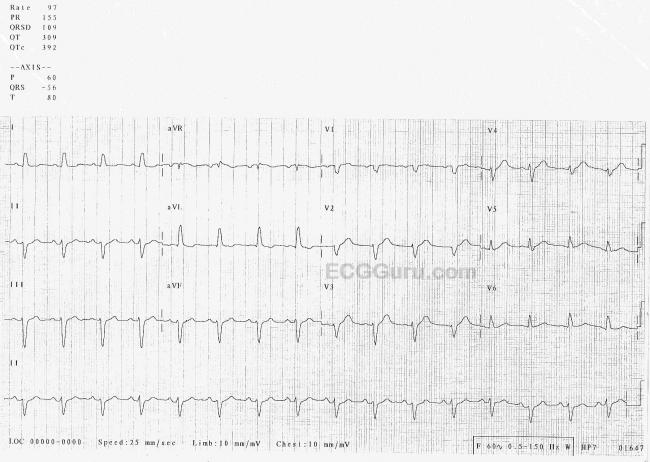
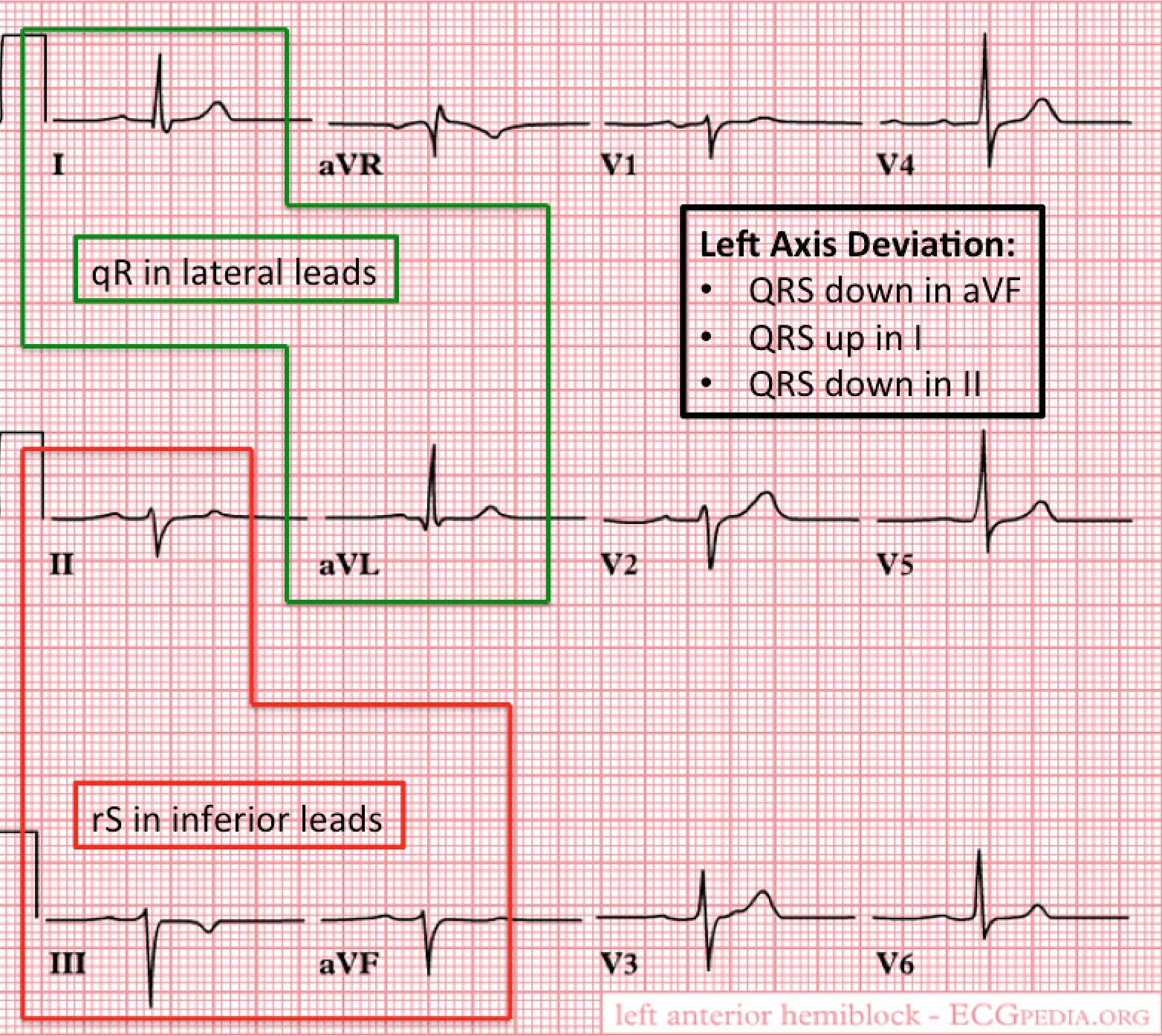
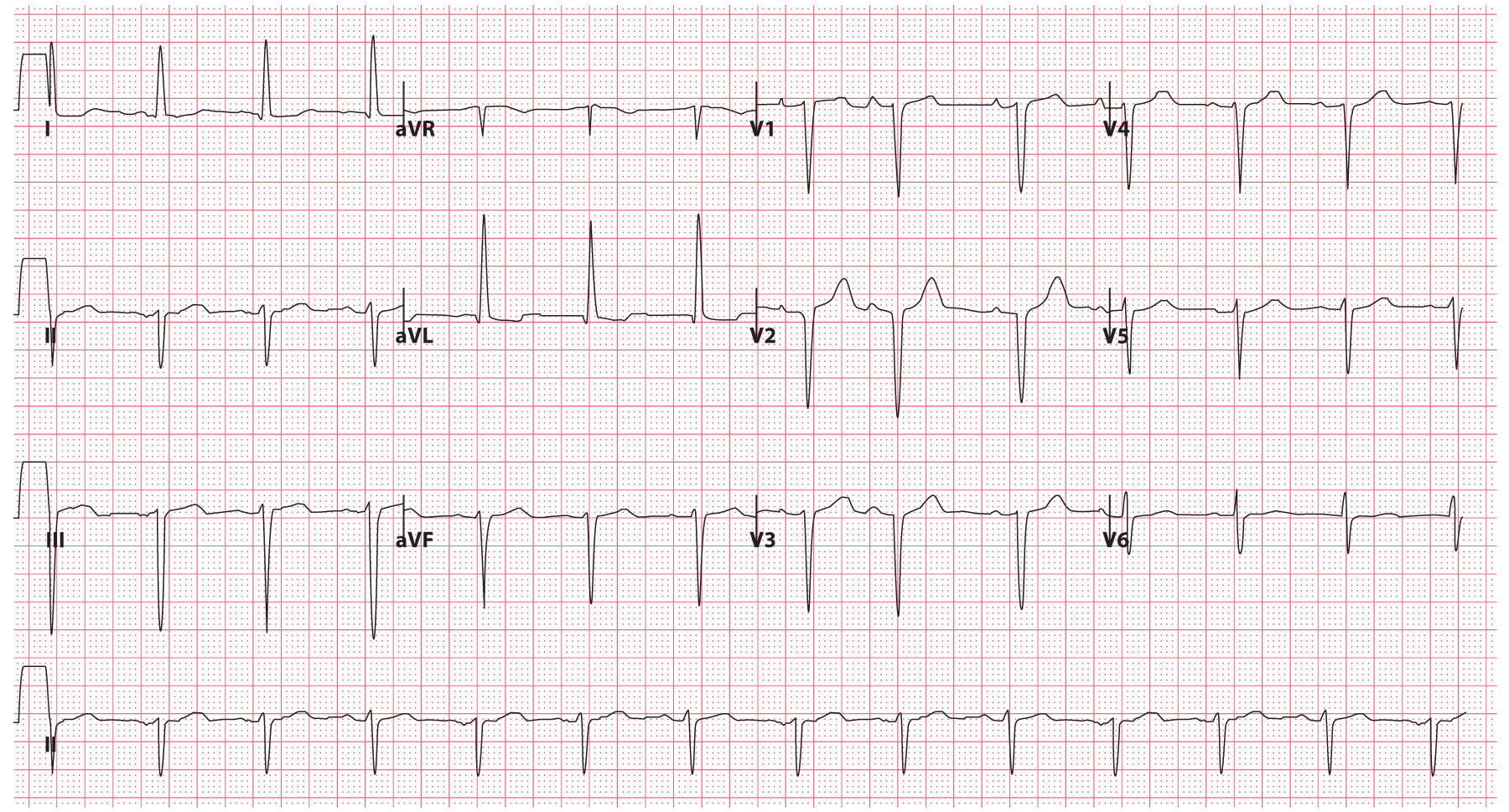
Left posterior fascicular block treatment. Left Posterior Fascicular Block LPFB ECG Review Right Bundle Branch Block RBBB ECG Review Second-Degree Atrioventricular AV Block Type I Wenkebach ECG Review. There is no known therapy to treat a left anterior fascicular block. ECG criteria for left posterior fascicular block LPFB Electrical axis 90 to 180.
This recommendation was accepted by. Reducing the intake of fats and carbohydrates is. The clinical presentation significantly depends on the extent of coronary artery vessel occlusion.
Bifascicular blocks require no direct treatment unless intermittent 2nd- or 3rd-degree AV block is present. QR complexes in inferior leads II III and aVF. QRS duration.
Q-wave is mandatory in leads III and aVF. Modest widening of the QRS complex. Individual symptoms may be addressed and treated.
Some of the common treatment protocols for the management of left anterior fascicular block include Complete cardiac evaluation is imperative to know the complete extent of the condition Specialized diet considerations are required. A left posterior fascicular block is a very rare abnormality of the cardiac conduction system and is primarily associated with a myocardial infarction of the inferior wall and coronary artery disease. A biventricular pacemaker is a battery-powered device used to balance.
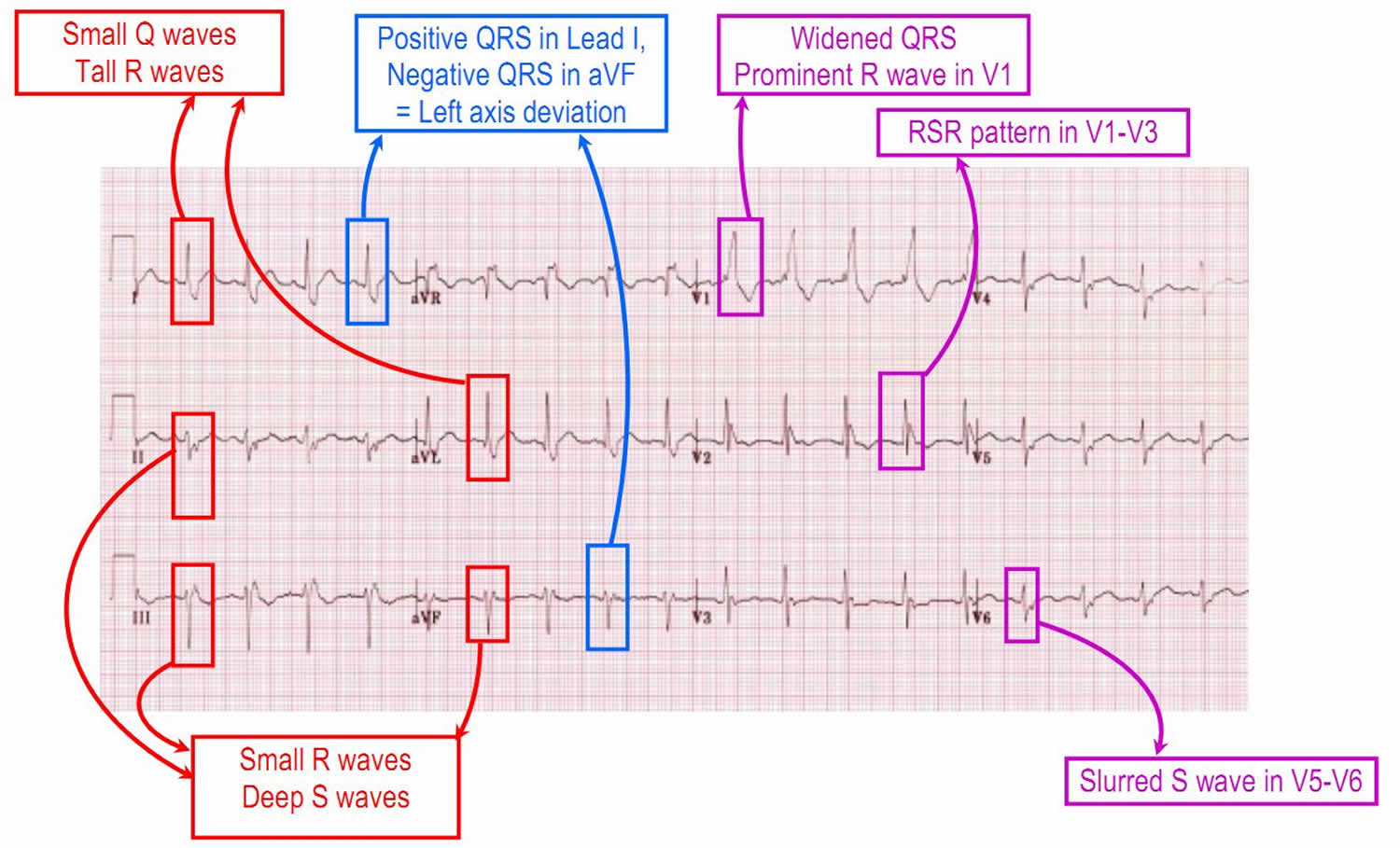
Left posterior fascicular block LPFB a pattern formerly called left posterior hemiblock seen on the surface electrocardiogram ECG results when normal electrical activity in the His-Purkinje system is delayed or interrupted. However a biventricular pacemaker also known as cardiac resynchronization therapy may be used to help prevent heart failure associated with this disorder according to University of California San Francisco. Bifascicular block involving the right bundle branch and left anterior fascicle is more common than right bundle branch block RBBB and left posterior fascicular block LPFB.
Syncope patients were recommended prophylactic pacemaker treatment because syncope is a predictor of subsequent development of highdegree AV block 19. 2629 Demoulin et al.
The clinical presentation significantly depends on the extent of coronary artery vessel occlusion.
QRS duration. The three possibilities are a LASFB and a RBBB a LPIFB and a RBBB or a left bundle branch block as this is impairment of both the LPIF and LASF. ECG criteria for left posterior fascicular block LPFB Electrical axis 90 to 180. Syncope patients were recommended prophylactic pacemaker treatment because syncope is a predictor of subsequent development of highdegree AV block 19. Left Anterior Fascicular Block Treatment. Reduction or complete elimination of smoking and alcohol since these habits cause vasoconstriction and further compromise blood circulation. A left posterior fascicular block is a very rare abnormality of the cardiac conduction system and is primarily associated with a myocardial infarction of the inferior wall and coronary artery disease. 1 Despite the fact that little is known about the long-term prognosis associated with LAFB it has generally been thought of as a benign electrocardiographic ECG finding. The clinical presentation significantly depends on the extent of coronary artery vessel occlusion.
Left anterior fascicular block LAFB is considered a failure or delay of conduction in the left anterior fascicle. Isolated monofascicular blocks are benign and require no treatment. 2629 Demoulin et al. A left posterior fascicular block is a very rare abnormality of the cardiac conduction system and is primarily associated with a myocardial infarction of the inferior wall and coronary artery disease. Individual symptoms may be addressed and treated. 2 This view was recently challenged in an article by Mandyam et al 3 which reported an association between LAFB. QR complexes in the inferior leads.
























Posting Komentar untuk "Left Posterior Fascicular Block Treatment"