 Nutrition Through the Life Cycle 5th Edition Brown Test Bank
Nutrition Through the Life Cycle 5th Edition Brown Test Bank6 Health risks of being underweight There is a lot of interest in the medical world in the health effects of being overweight, but what about the effects of being underweight? There are certain health risks associated with low weight or poor nutrition. These risks include: Keep reading to learn more about these risks of being underweight, as well as how to identify if you are underweight, what symptoms you can experience and how you can find help. Your doctor may help you and your doctor determine if you are underweight. BMI is an estimate of body fat based on its height and weight. BMI rangeWeight below 18.5 underweight18.5-24,9normal25-29.9 overweight30 or higher aobese There are some limitations to determine your health using BMI alone. If you have low weight, you may not be eating enough healthy foods with key nutrients to feed your body. That can cause malnutrition. Over time, malnutrition can affect your health in several different ways that can be perceptible to you or those around you. Symptoms may include: A from Japan compared the dietary habits of women with low weight with the desire to be thin women with low weight without this desire. They found that women with a desire to be thin had less healthy eating habits than women with low weight who did not have this desire. If you have low weight, it is more likely that you are also malnourished if your low BMI is caused by a unbalanced diet or an underlying disease that affects nutrient absorption. Malnutrition can also cause anemia or deficiency in essential vitamins. Anemia can also be caused by poor absorption of nutrients. A of studies found a connection between increased infection and being underweight. Researchers pointed out their difficulty in determining whether this is a result of being underweight or whether it has more to do the underlying causes to be low weight. For example, malnutrition can lead to a decrease in immune function and also cause people to be underweight. More research is needed to fully understand the connection between weight and immune function. Evidence was found that people with lower weight than normal who had total knee replacement surgery were more likely to develop infections after surgery than people who were not underweight. Although they could not determine the reasons for this, they believe that people with low weight are not able to heal wounds, as well as people with a normal BMI. They also found that the low-weight group had a low preoperative hemoglobin. While more research is needed, findings suggest that low weight can affect your ability to heal wounds. Another found greater complications in people with lower weight than normal who had full hip replacement surgery compared to normal weight people. Complications that follow and also seem to be higher for people who are underweight. Researchers have also linked to low BMI to higher incidences of postoperative deaths in the first year after BMI. Low body weight can increase your risk of low bone mineral density (BMD) and osteoporosis. One looked at MMD in 1,767 premenopausal women, and found that 24 per cent of women with a BMI of 18.5 or lower had a low MMD. Only 9.4 per cent of participants with a BMI higher than 18.5 had DMO. The results of the study suggest that low weight increases the risk of osteoporosis. Women with low BMI are at greater risk for , which is a lack of menses, and other dysfunctions in the menstrual cycle. Irregular or lost menstrual cycles can be an indicator of , or are not ovulating. Chronic anovulation can cause infertility. If you are trying to conceive and are under weight, talk to your doctor. They can do a simple blood test to see if you are regularly ovulating. They can also test other signs of infertility. Your doctor may recommend a healthy weight before you become pregnant. Being underweight while pregnant may pose risks to your baby. That's why it's important to keep a healthy weight during pregnancy. Developmental delays can be seen in low-weight children, especially children under the age of 3 when the brain is rapidly developing. The brain needs nutrients to develop properly. Low-weight children may lack key nutrients due to malnutrition and malabsorption. This can affect brain development and cause delays in development milestones. Your child's pediatrician will trace your child's growth in well-visited appointments. They will use these measurements to see how your child compares to the average growth of other children of your age, and how your child's percentages change over time. If your child's growth rate decreases, that may be a warning sign that they are not gaining weight at the expected rate. For example, if your child is in the 45th percentile to his 12-month appointment and the 35th percentile to his 15-month appointment, your doctor may be worried about his weight gain. Your child's pediatrician will also ask about development milestones during regular visits. Remember that not all the children reached milestones at the same time. Instead, doctors look to see if your child is hitting them within a certain range of time. For example, some children take their first steps when they have less than a year, while others do not start walking until they are several months in their first year. Learning to walk or talk later will not point to a problem unless your child is also late with other milestones. If you suspect that you are underweight, make an appointment with your primary care doctor or dietitian. Your doctor may examine your medical history and help identify any problems that may lead to poor nutrition or weight loss. Before your appointment, you may want to ask yourself: Share the answers to these questions with your doctor. If your doctor rules out any serious underlying medical problems, you can identify an objective weight. From there, you can come to a plan to help you achieve that weight through healthy eating and other appropriate treatments. With the help of your doctor, you can be able to reach a normal BMI through lifestyle changes and healthy eating. Your doctor may also help you navigate solutions for limited access to nutritious dense foods, psychological problems, underlying health conditions, side effects of medicines and other situations that contribute to being underweight or malnourished. By making some adjustments to your diet and lifestyle, you can gain healthy weight and avoid the negative health effects of being underweight. Last medical review on April 17, 2017Read this following
Please check that you're a human Access to this page has been denied because we believe it is using automation tools to navigate the page website. This may occur as a result of the following: Please make sure that Javascript and cookies are enabled in your browser and you are not blocking them to carry. Reference ID: #5e636c60-822f-11eb-8f51-69e5b1046ea8 Powered by Inc.

Underweight health risks: Causes, symptoms, and treatment
Nutrition Through the Life Cycle 5th Edition Brown Test Bank:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/underweight-while-pregnant-4589291_final2-cad7024e794947c4a6097b135c6d57e8.png)
What to Know If You Are Underweight While Pregnant
Underweight Health Risks: What You Should Know
Nutrition Chapter 8: 2 Flashcards | Quizlet
Post Test: Continuing Education Module
Underweight Health Risks: What You Should Know
Obesity: Definition, Causes, Diagnosis, Treatment & More
Effectiveness of the Healthy Lifestyles Programme (HeLP) to prevent obesity in UK primary-school children: a cluster randomised controlled trial - The Lancet Child & Adolescent Health
Weight loss and BMI criteria in GLIM's definition of malnutrition is associated with postoperative complications following abdominal resections – Results from a National Quality Registry - Clinical Nutrition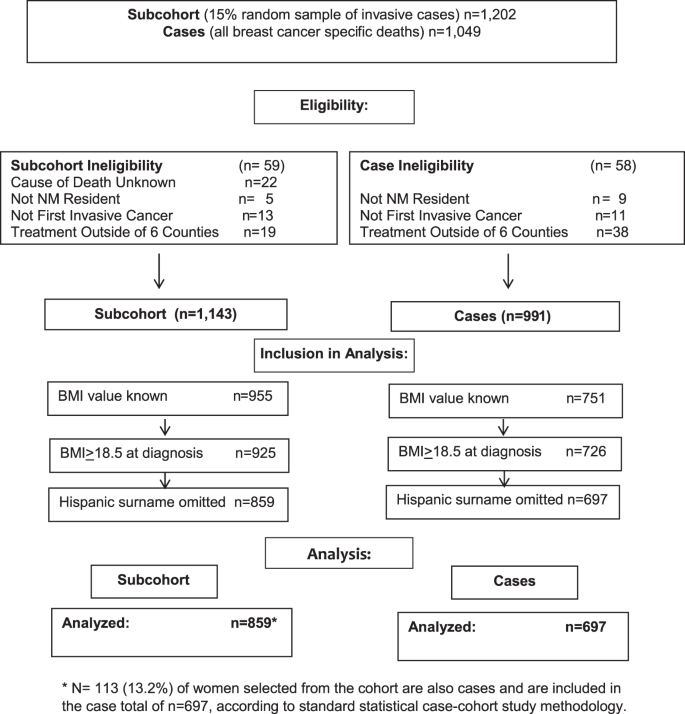
Obesity and survival among a cohort of breast cancer patients is partially mediated by tumor characteristics | npj Breast Cancer
Defining diet quality: a synthesis of dietary quality metrics and their validity for the double burden of malnutrition - The Lancet Planetary Health
Expert panel report: Guidelines (2013) for the management of overweight and obesity in adults - 2014 - Obesity - Wiley Online Library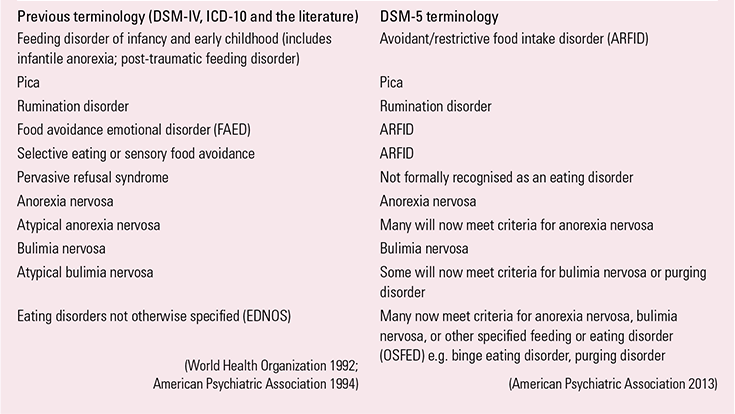
Atypical early-onset eating disorders | Advances in Psychiatric Treatment | Cambridge Core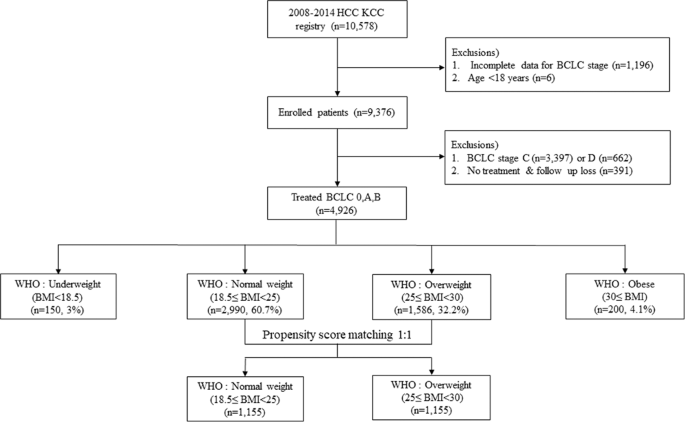
Survival Outcomes According to Body Mass Index in Hepatocellular Carcinoma Patient: Analysis of Nationwide Cancer Registry Database | Scientific Reports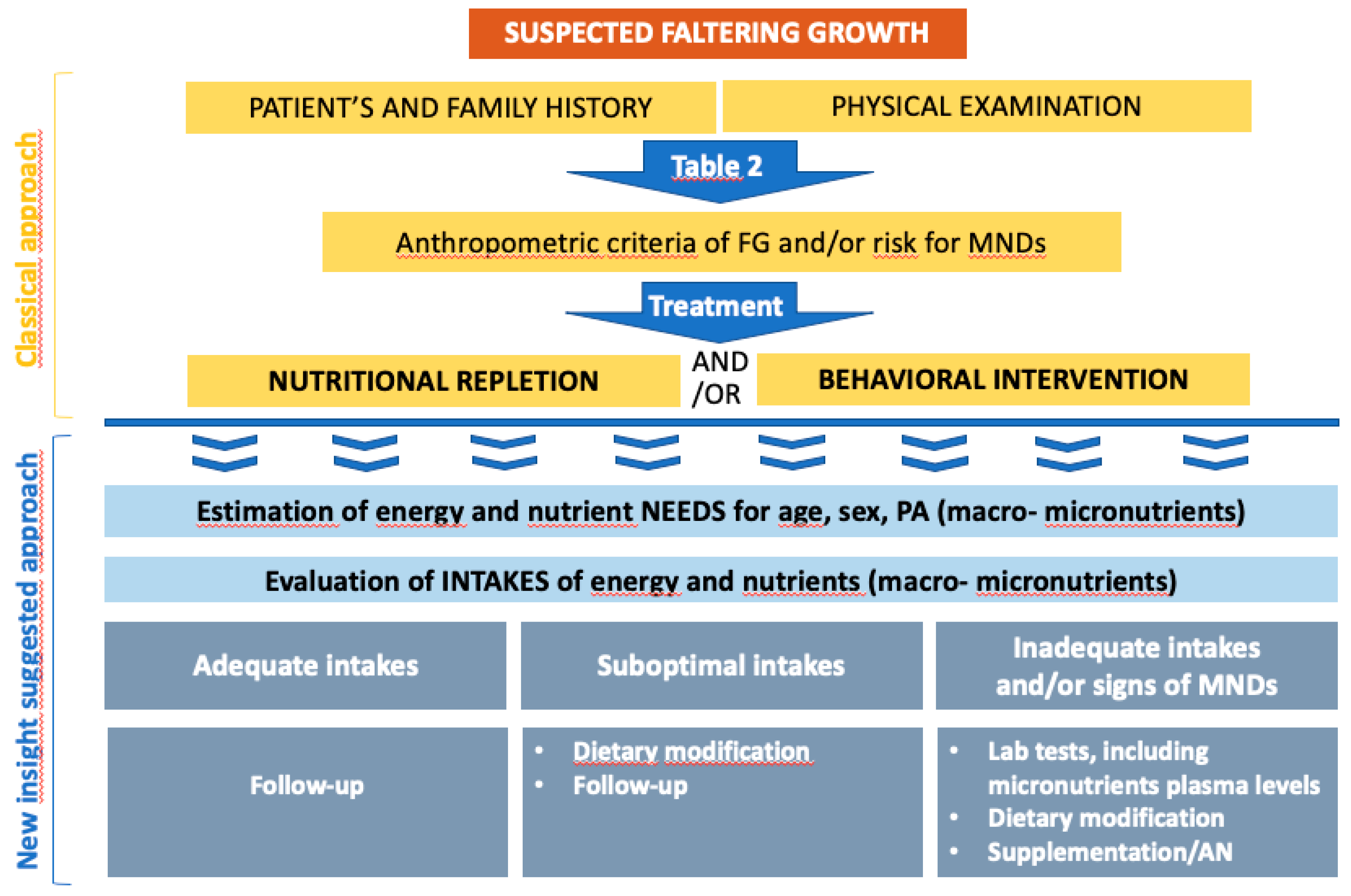
Nutrients | Free Full-Text | Failure to Thrive in the Outpatient Clinic: A New Insight | HTML
Association of BMI with overall and cause-specific mortality: a population-based cohort study of 3·6 million adults in the UK - The Lancet Diabetes & Endocrinology
Examining the Role of Weight Status and Individual Attributes on Adolescent Social Relations
The COVID-19 Pandemic Lockdowns and Changes in Body Weight among Polish Women. A Cross-Sectional Online Survey PLifeCOVID-19 Stu
Expert panel report: Guidelines (2013) for the management of overweight and obesity in adults - 2014 - Obesity - Wiley Online Library
Nutrients | Free Full-Text | Maternal Diet During Pregnancy and Blood Cadmium Concentrations in an Observational Cohort of British Women | HTML
Underweight patients are at just as much risk as super morbidly obese patients when undergoing anterior cervical spine surgery - The Spine Journal
Expert panel report: Guidelines (2013) for the management of overweight and obesity in adults - 2014 - Obesity - Wiley Online Library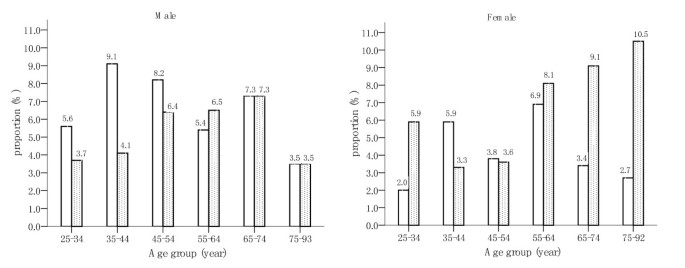
Risk factors for overweight and obesity, and changes in body mass index of Chinese adults in Shanghai | BMC Public Health | Full Text
About Adult BMI | Healthy Weight, Nutrition, and Physical Activity | CDC
GLOBAL HEALTH RISKS
IJERPH | Free Full-Text | Exploring Mediation Roles of Child Screen-Viewing between Parental Factors and Child Overweight in Taiwan | HTML
Adiposity change and mortality in middle-aged to older Chinese: an 8-year follow-up of the Guangzhou Biobank Cohort Study | BMJ Open
Mapping of variations in child stunting, wasting and underweight within the states of India: the Global Burden of Disease Study 2000–2017 - EClinicalMedicine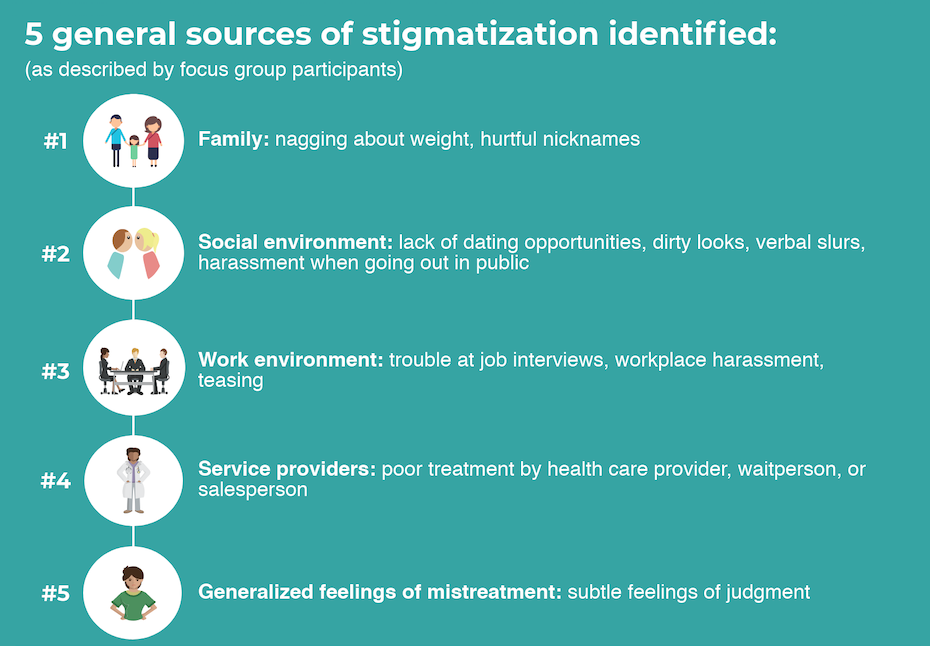
Overweight and Underweight—What are the Risks? – Nutrition: Science and Everyday Application
IJERPH | Free Full-Text | Is Adiposity Associated with the Quality of Movement Patterns in the Mid-Adolescent Period? | HTML
Expert panel report: Guidelines (2013) for the management of overweight and obesity in adults - 2014 - Obesity - Wiley Online Library
Public Health Principles (Section II) - Health in Humanitarian Emergencies
IJERPH | Free Full-Text | Efficacy of an Internet-Based Intervention to Promote a Healthy Lifestyle on the Reproductive Parameters of Overweight and Obese Women: Study Protocol for a Randomised Controlled Trial |
Body mass index and all‐cause mortality in older adults: A scoping review of observational studies - Javed - 2020 - Obesity Reviews - Wiley Online Library
A randomized controlled trial for overweight and obesity in preschoolers: the More and Less Europe study - an intervention within the STOP project | BMC Public Health | Full Text
Healthy Foods To Include In your Weight Gain Diet Chart | Femina.in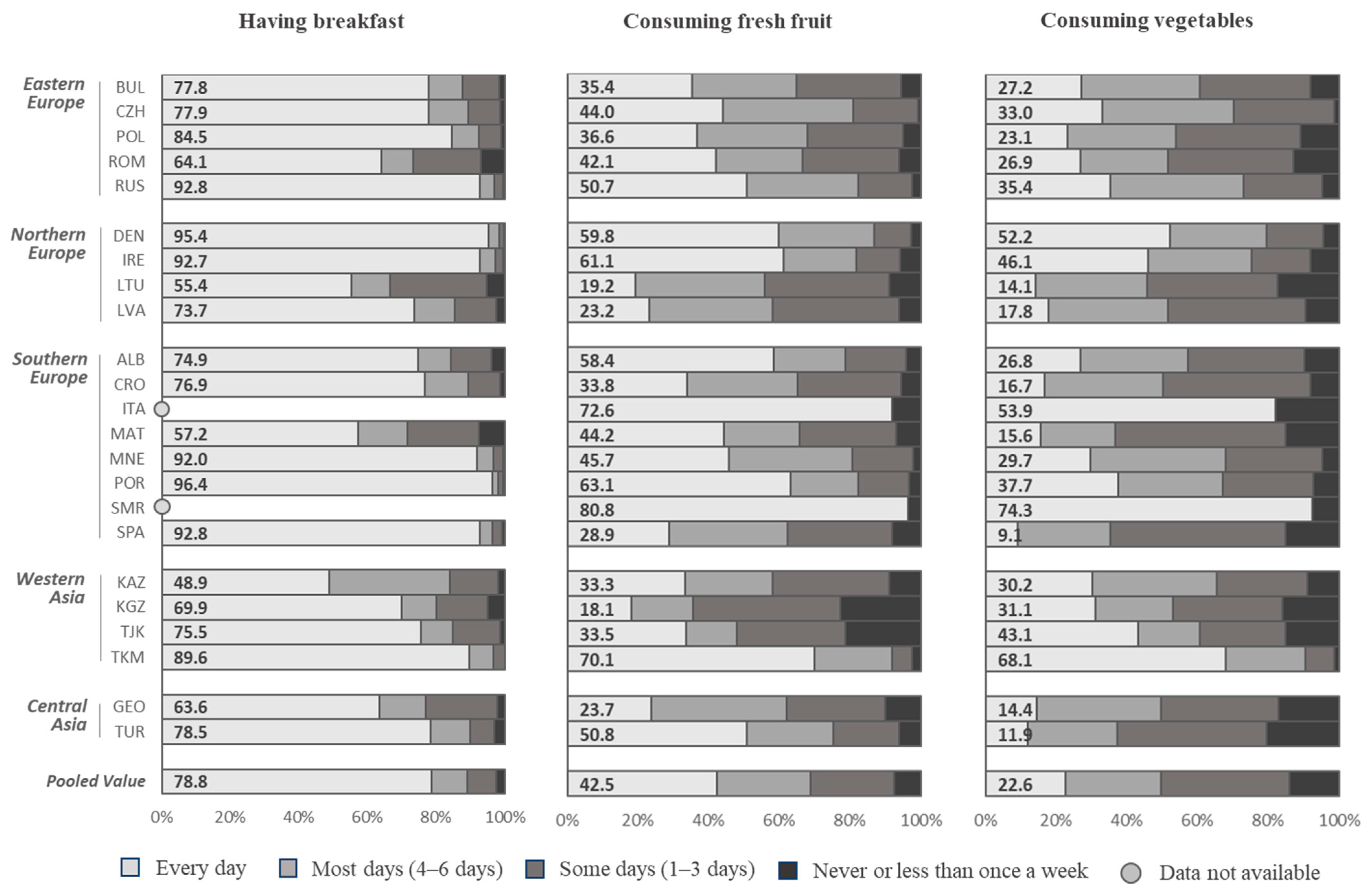
Nutrients | Free Full-Text | A Snapshot of European Children's Eating Habits: Results from the Fourth Round of the WHO European Childhood Obesity Surveillance Initiative (COSI) | HTML
n-6 cover sd
 Nutrition Through the Life Cycle 5th Edition Brown Test Bank
Nutrition Through the Life Cycle 5th Edition Brown Test Bank

:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/underweight-while-pregnant-4589291_final2-cad7024e794947c4a6097b135c6d57e8.png)































Posting Komentar untuk "the known health risks for being underweight include all of the following except"